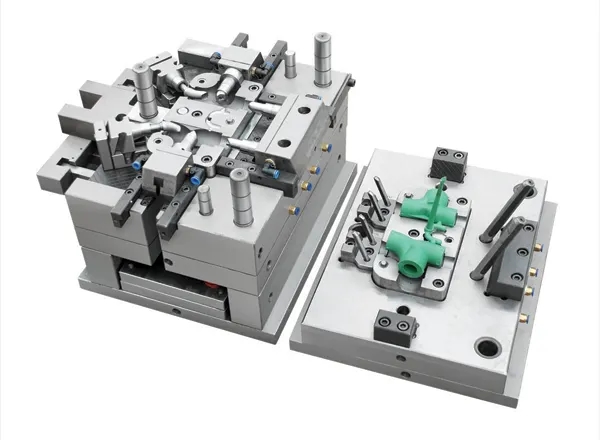
When it comes to molds, people often associate die-casting molds with injection molds. In fact, the difference between the two is very big. Dry die casting is to fill the mold cavity with liquid or semi liquid metal at a very high speed and solidify under pressure to obtain die castings. It is generally used for metal materials, while injection molding is the main method of thermoplastic molding. Thermoplastic is made of thermoplastic resin, which can be repeatedly heated, softened, cooled and solidified. It is a physical process, reversible, that is, it can be used as recycled plastic. Although both of them need to use mold molding to make products, although the working principle is not different, the materials are different, and the natural molds are also different. Let's talk about the difference between die-casting mold and injection mold!
1. the injection pressure of the die-casting mold is large, so the mold template is required to be relatively thick to prevent deformation.
2. the gate of the die-casting die is also different from that of Wang Su's die. It should be the high pressure that needs to be used to split the material flow with a splitter cone.
3. there is no need to quench the die core of the die-casting mold, because the temperature in the mold cavity is relatively high during die-casting, which is equivalent to a quench, while the injection mold needs to be quenched.
4. the mold cavity of the die-casting die shall be nitrided to prevent alloy mucous membrane cavity.
5. generally, the corrosion of die-casting die is relatively large, and the outer surface is generally subject to bluing treatment.
6. injection molds generally rely on thimbles, and the split type can exhaust. The die-casting molds must be provided with exhaust slots and slag collecting bags.
7. the requirements for split type matching of die-casting mold are higher. The alloy fluidity is much better than that of plastic. It will be very dangerous for high temperature and high pressure flowing materials to fly out of the split type.
8. compared with the injection mold, the fitting clearance of the movable distribution part of the die-casting mold is larger, because the high temperature of the die-casting process will cause thermal expansion. If the clearance is too small, the mold will be stuck.
